MBBR Process Flow and Application Scope
By: Kate Nana
Post Date: April 11, 2025
Post Tags: MBBR Process Flow and Application Scope,Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)

MBBR, or Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor, is a very eye-catching presence on the big stage of sewage treatment. It can be seen in the sewage generated in our daily life and various industrial wastewater treatment fields.
I. Working Principle of MBBR
To understand how MBBR(Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) works, we must first grasp its core - biofilm technology. Think about it, in this reactor, there are many suspended carriers. These carriers are like "small houses" for microorganisms, providing them with a place to settle down and attach. Moreover, these carriers swim freely in the reactor, and the microorganisms take root and reproduce on them, and slowly form a layer of biofilm. The "bad guys" such as organic matter and ammonia nitrogen in the sewage are "cleaned up" by this layer of biofilm through adsorption, degradation and other means.
Biofilm Formation:
At the beginning, the microorganisms are like a group of small "explorers", who gradually find the surface of the carrier and then begin to "settle down". As time goes by, more and more microorganisms gather and the biofilm becomes thicker and thicker, until finally, the growth and shedding of microorganisms reach a state of equilibrium and no longer thickens indefinitely.
Pollutant Removal:
After the sewage flows into the reactor, it comes into "close contact" with the biofilm. The microorganisms are like hardworking "cleaners". Through their own metabolic activities, they decompose the organic matter in the sewage clearly. In the end, these organic matter becomes carbon dioxide, water, and some inorganic salts, which are all harmless to the environment.
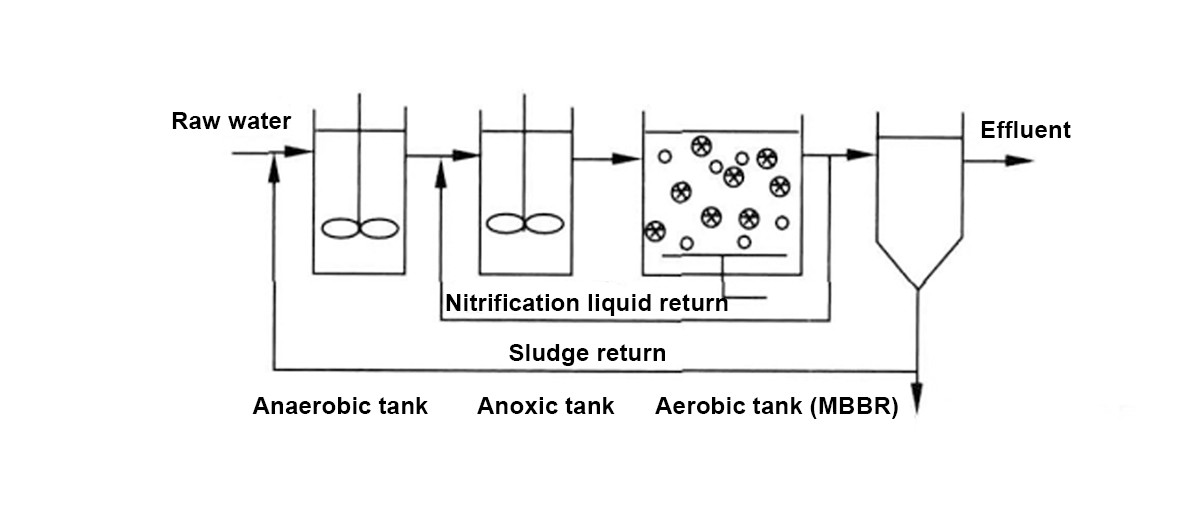
II. MBBR Process Flow
The process flow of MBBR is actually not difficult to understand. It is roughly the following steps:
Water inlet link
The sewage "runs" into the MBBR(Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) reactor along the water inlet pipe. As soon as it enters, it starts a "mixing party" with the carrier inside and is fully mixed together.
Aeration operation
At this time, the aeration system begins to work. It continuously delivers oxygen to the reactor. On the one hand, this oxygen is used for the microorganisms to "breathe" and give them strength to work; on the other hand, it can also keep the carriers in the reactor in a suspended state and prevent them from sinking.
Biodegradation stage
The microorganisms on the biofilm are very active. Once they come into contact with the pollutants in the sewage, they immediately start working, adsorbing these pollutants and then degrading them bit by bit.
III. Features of MBBR(Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor)
Efficient biological treatment capacity
The carrier of MBBR has a particularly powerful feature, that is, the specific surface area is particularly large. This means that there are more places for microorganisms to attach. With more microorganisms, the ability to treat sewage is naturally stronger, and pollutants in sewage can be treated more quickly and effectively.
Super strong impact load resistance
The actual sewage situation is ever-changing, and the water quality of the influent often fluctuates. But MBBR is not "afraid" at all. It adapts well to such changes. Even if a high concentration of organic pollutants suddenly comes, it can respond steadily and treat sewage normally.
Easy to operate and maintain
In actual operation, the MBBR process does not require particularly complex operations. The staff does not need to keep an eye on it all the time, nor do they need to perform various complex operations frequently. And it does not require much maintenance work, and does not require too much time and energy to maintain.
Small footprint
Compared with the traditional activated sludge method, MBBR saves space. If the traditional method is used, it may require a large area to build a treatment facility, but MBBR can complete the same sewage treatment task in a relatively small space, which is very friendly to those places with tight land resources.
Relatively low energy consumption
MBBR does not require a particularly large amount of aeration when it is in operation. With less aeration, less energy is consumed, which can help us save a lot of electricity bills. In the long run, it can reduce a lot of operating costs.
IV. Application Scope of MBBR(Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor)
MBBR has many application scenarios, and the following are more common ones:
Domestic sewage treatment
In cities, MBBR can treat domestic sewage produced every day very well. It can remove common pollutants such as organic matter and ammonia nitrogen in sewage, so that the treated water meets the discharge standards and will not pollute the environment.
Industrial wastewater treatment
Industrial enterprises such as pharmaceutical factories, chemical plants, and food processing plants will produce various wastewaters, and many of them are high-concentration organic wastewaters, which are not easy to treat. But MBBR can come in handy. It has enough ability to treat these difficult-to-treat industrial wastewaters to meet the standards, allowing enterprises to produce environmentally friendly.
Rural sewage treatment scenarios
In rural areas, sewage is generally more scattered. The characteristics of MBBR are very suitable for this situation. It can operate "small and beautiful" in various villages, treat rural domestic sewage well, and improve the rural environment.
Black and smelly water body restoration work
Nowadays, there are black and smelly water bodies in many places, which makes people uncomfortable and affects the environment. MBBR technology can also play a big role in this regard. It can gradually improve the water quality of black and smelly water bodies and restore the vitality of water bodies.