MBBR Process Principles and Filler Evaluation Indicators
By: Kate Nana
Post Date:May 6th, 2025
Post Tags: MBBR :MBBR Process Principles and Filler Evaluation Indicators,Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)

Principles of MBBR Technology
The MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) process works by adding a certain quantity of suspended carriers to the reactor, increasing both the biomass and microbial diversity, thereby improving treatment efficiency. Since the density of the filler is close to that of water, it becomes fully mixed with the water during aeration, creating a microbial growth environment consisting of gas, liquid, and solid phases. The collision and shear forces between the carriers in the water break air bubbles into finer sizes, enhancing oxygen utilization.
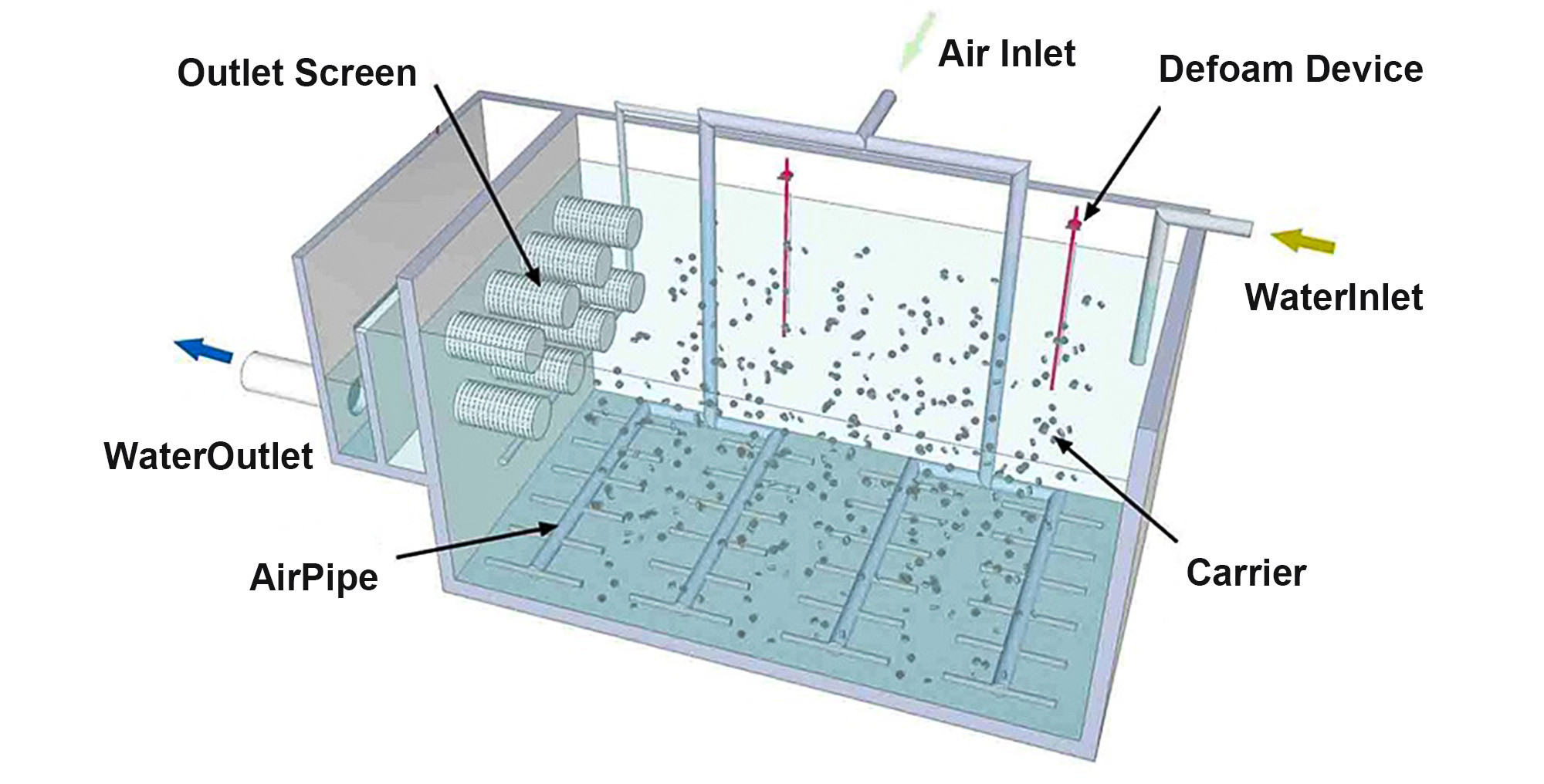
Additionally, each carrier develops different microbial communities on its interior and exterior surfaces. Anaerobic or facultative bacteria grow inside, while aerobic bacteria thrive outside, making each carrier a miniature reactor. This allows simultaneous nitrification and denitrification, improving overall treatment performance.
The MBBR process combines the advantages of traditional fluidized beds and biological contact oxidation methods, making it a novel and efficient wastewater treatment approach. Aeration and hydraulic lifting forces keep the carriers in a fluidized state, forming both suspended activated sludge and attached biofilm. This maximizes reactor space utilization, leveraging the strengths of both attached and suspended growth systems while compensating for their limitations. Unlike conventional fillers, the suspended carriers repeatedly interact with wastewater, earning them the name "moving biofilms."
Evaluation Indicators for MBBR Fillers
1. Biofilm Adhesion Capacity
- The ability of biofilm to adhere is the most critical criterion for evaluating filler quality.
- Biofilm attachment amount = Protected surface area (related to filler design and operating conditions) × Biofilm attachment per unit area (related to filler properties).
2. Filler Performance
- Filler performance is the most important factor in assessing biofilm attachment capacity.
-(1) Surface Properties
1. Surface Texture: Generally, higher surface roughness speeds up biofilm formation.
2. Surface Charge: Since microorganisms are typically negatively charged, a positively charged filler surface promotes microbial growth.
3. Hydrophilicity: Microorganisms are hydrophilic, so hydrophilic fillers facilitate biofilm attachment.
- (2) Hydraulic Performance
1. Porosity: Higher porosity is preferable for fillers.
2. Shape and Size: Affects the flow patterns of water and air.
- (3) Fluidization Performance: Related to filler density. The optimal density range is 0.97–1.03, allowing fluidization with minimal aeration or stirring.
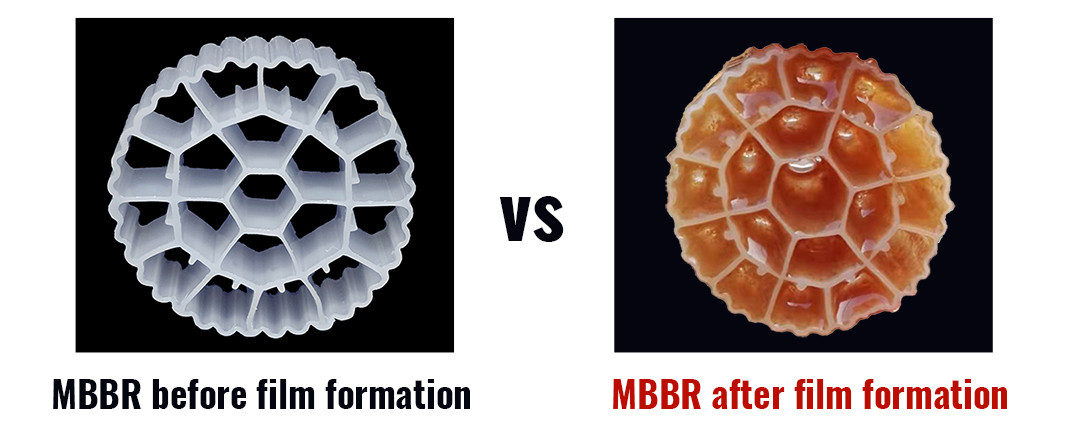
Mature Biofilm Identification
- Visual Inspection:
- A uniform biofilm distribution on the carrier surface, denser near the surface and looser farther out, along with a darkening color, indicates biofilm maturity.
- Microscopic Examination:
- A dense biofilm structure with diverse microbial species, dominated by sessile ciliates (e.g., Vorticella, Epistylis), and the presence of a small number of rotifers and free-swimming ciliates signify biofilm maturity.






