Structure and Components of a Chemical Dosing System
By: Kate Nana
Post Date: May 8th, 2025
Post Tags: Dosing System , Structure and Components of a Chemical Dosing System

A chemical dosing system is an integrated equipment designed for dosing, mixing, liquid transportation, and automatic control. It is used in circulating water systems that require the addition of corrosion inhibitors, scale inhibitors, and biocides to achieve precise dosing and measurement of water treatment chemicals.
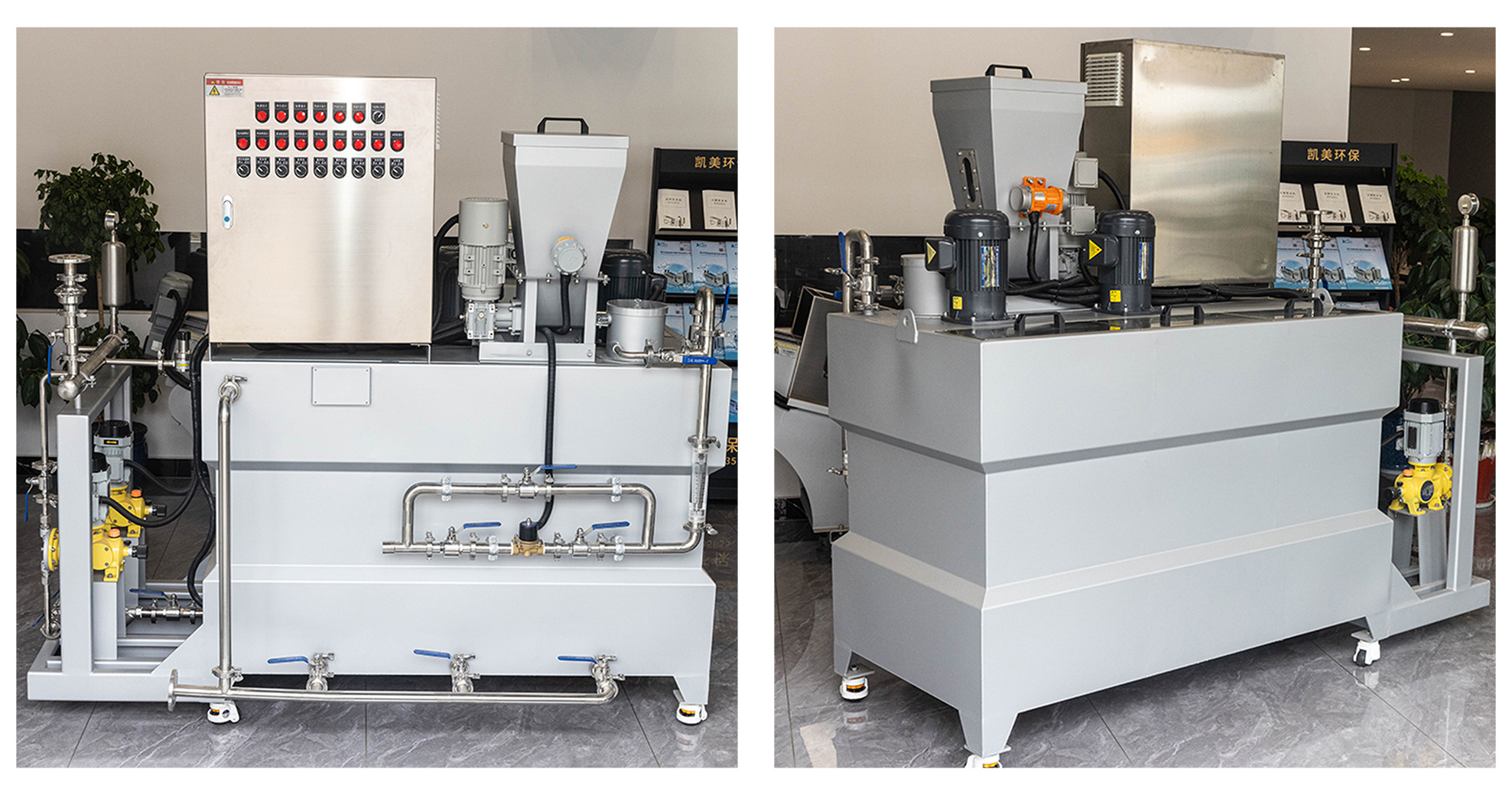

The automatic chemical dosing system mainly consists of the following components:
1. Chemical Storage Tank: Used to store chemicals, typically equipped with an automatic stirring system to maintain uniformity.
2. Dosing System: Precisely controls the amount of chemical added as needed.
3. Mixing System: Blends the dosed chemical with water or other media.
4. Control System: Manages the operation of the entire system, including startup, shutdown, and fault detection.
5. Safety Protection System: Ensures the system can automatically shut down or activate in case of abnormalities.
6. Power Supply and Pump System: Provides electrical power and driving force for the entire system, with pumps used to transport chemicals from the storage tank to the mixing system.
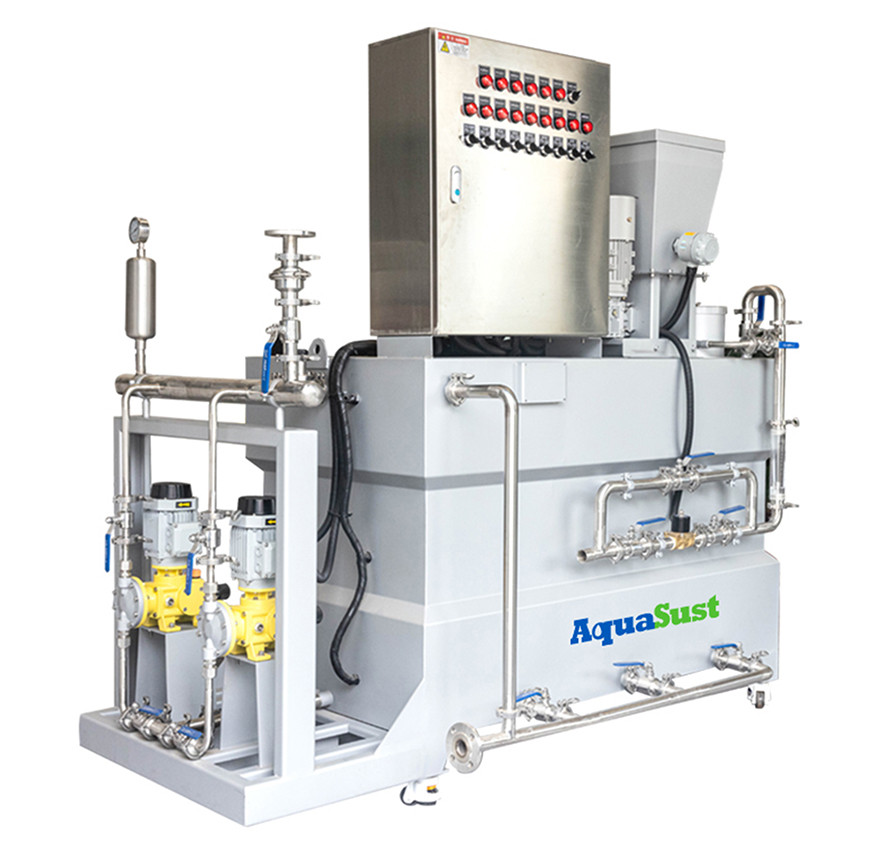

1. Chemical Storage Tank
The chemical storage tank is used to hold chemicals and is usually equipped with an automatic stirring system to maintain uniformity.
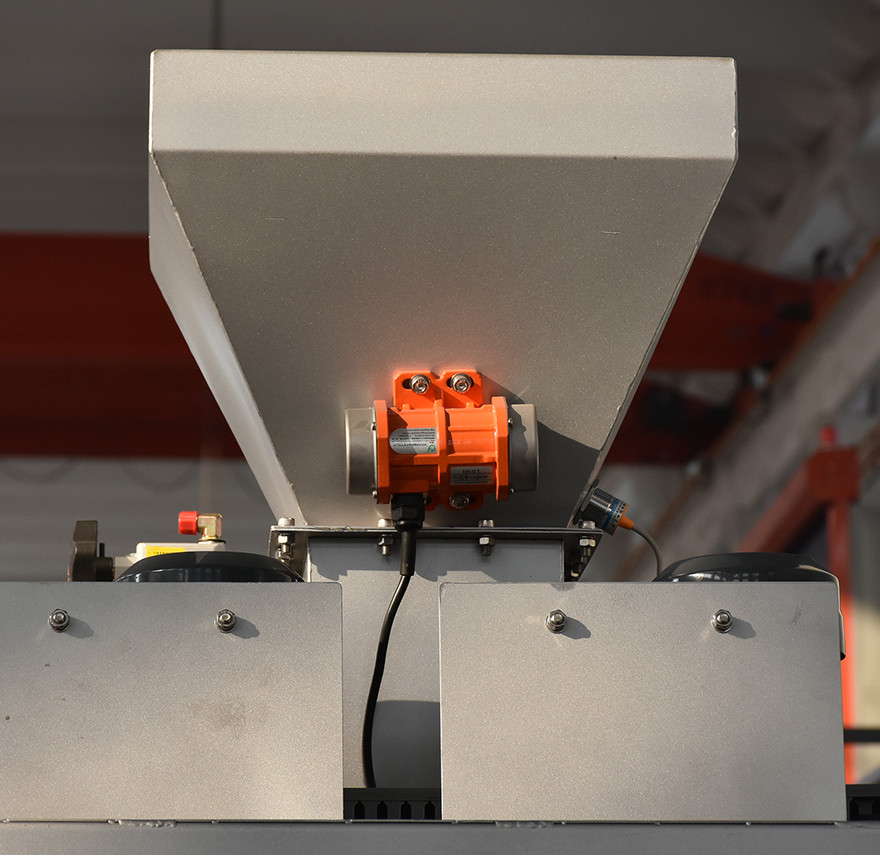
2. Dosing System
The dosing system is the core part of the automatic chemical dosing system. Its function is to accurately measure the required amount of chemical based on preset ratios or concentrations. Common dosing methods include mass dosing (using load cells) and volumetric dosing (using flow meters). To ensure accuracy, the dosing system requires regular calibration and maintenance.
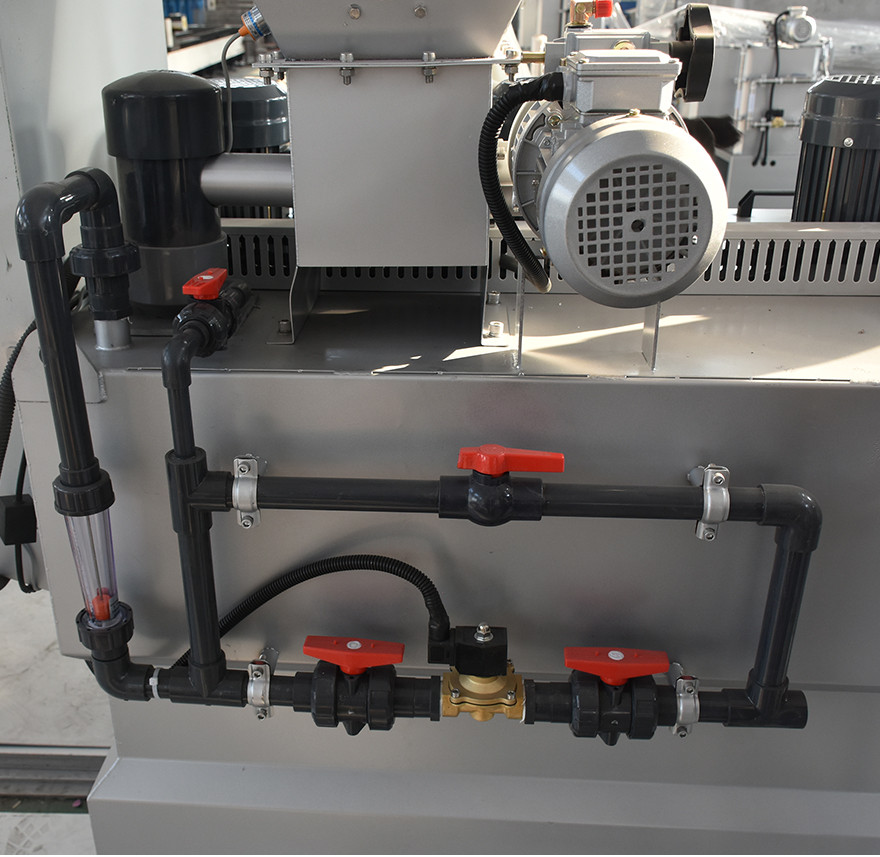
3. Mixing System
The mixing system ensures uniform blending of the dosed chemical with water or other media. Various mixing methods are available, such as pipeline mixing and static mixer blending. Static mixers are a common mixing device that utilizes fluid interactions within the pipeline to achieve rapid and uniform mixing.
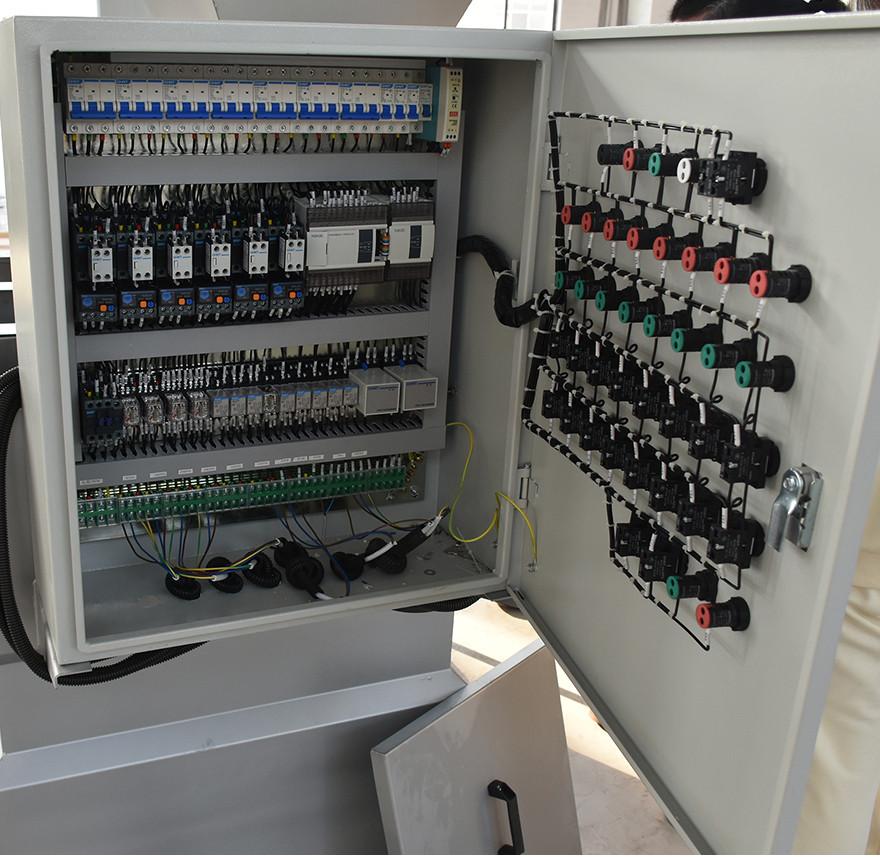

4. Control System
The control system acts as the "brain" of the automatic dosing system, receiving and processing input signals to operate the system according to preset programs. It typically includes a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), touchscreen interface, relays, and other components. Through programming, functions such as startup, shutdown, and fault detection can be automated, while real-time monitoring of system status and parameters is displayed.

5. Safety Protection System
The safety protection system ensures that the system automatically takes protective measures in abnormal conditions to prevent accidents or minimize damage. Common safety measures include overload protection, short-circuit protection, and phase-loss protection. This system consists of various sensors and actuators that continuously monitor the system's operation and trigger protective actions when anomalies are detected.
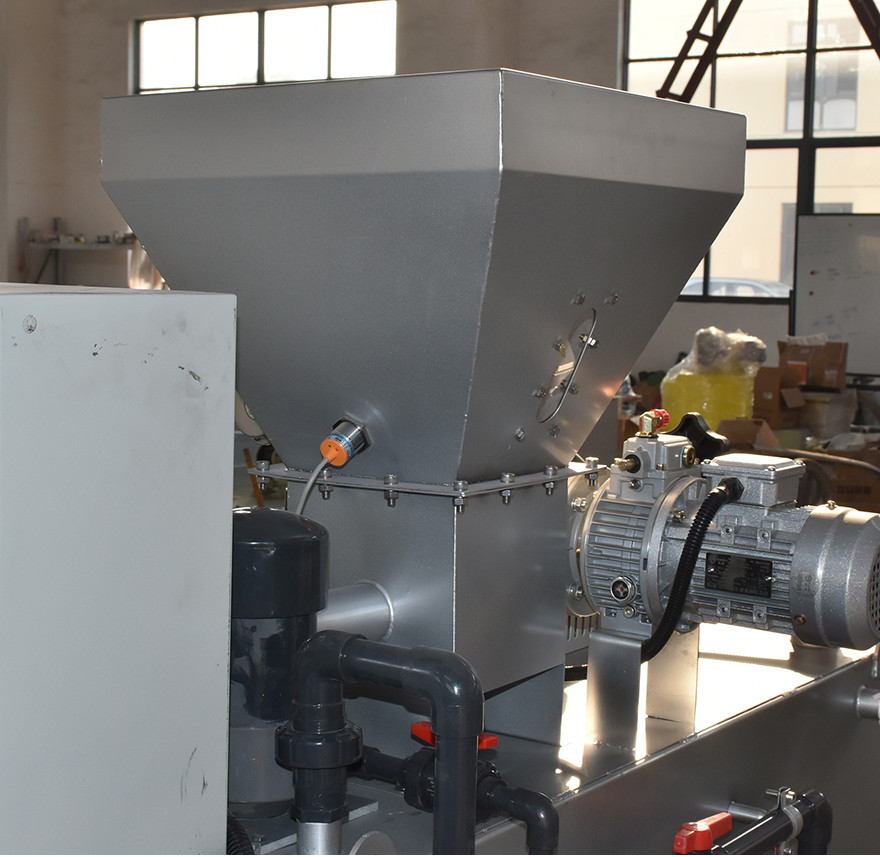

6. Power Supply and Pump System
The power supply and pump system provides electrical power and driving force for the entire system. The power supply is usually connected to the mains, while the pump system transports chemicals from the storage tank to the mixing system. Depending on the application and chemical properties, different types of pumps (e.g., centrifugal pumps, diaphragm pumps) can be selected. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure reliable operation.





