Working principle and application of tube settler
By: Kate Nana
Post Date:April 7, 2025
Post Tag:Working principle and application of tube settler

I. Working Principle
Shallow Depth Sedimentation Theory
For a given effective volume of the sedimentation tank, the shallower the tank, the larger the sedimentation area, and the higher the removal efficiency.
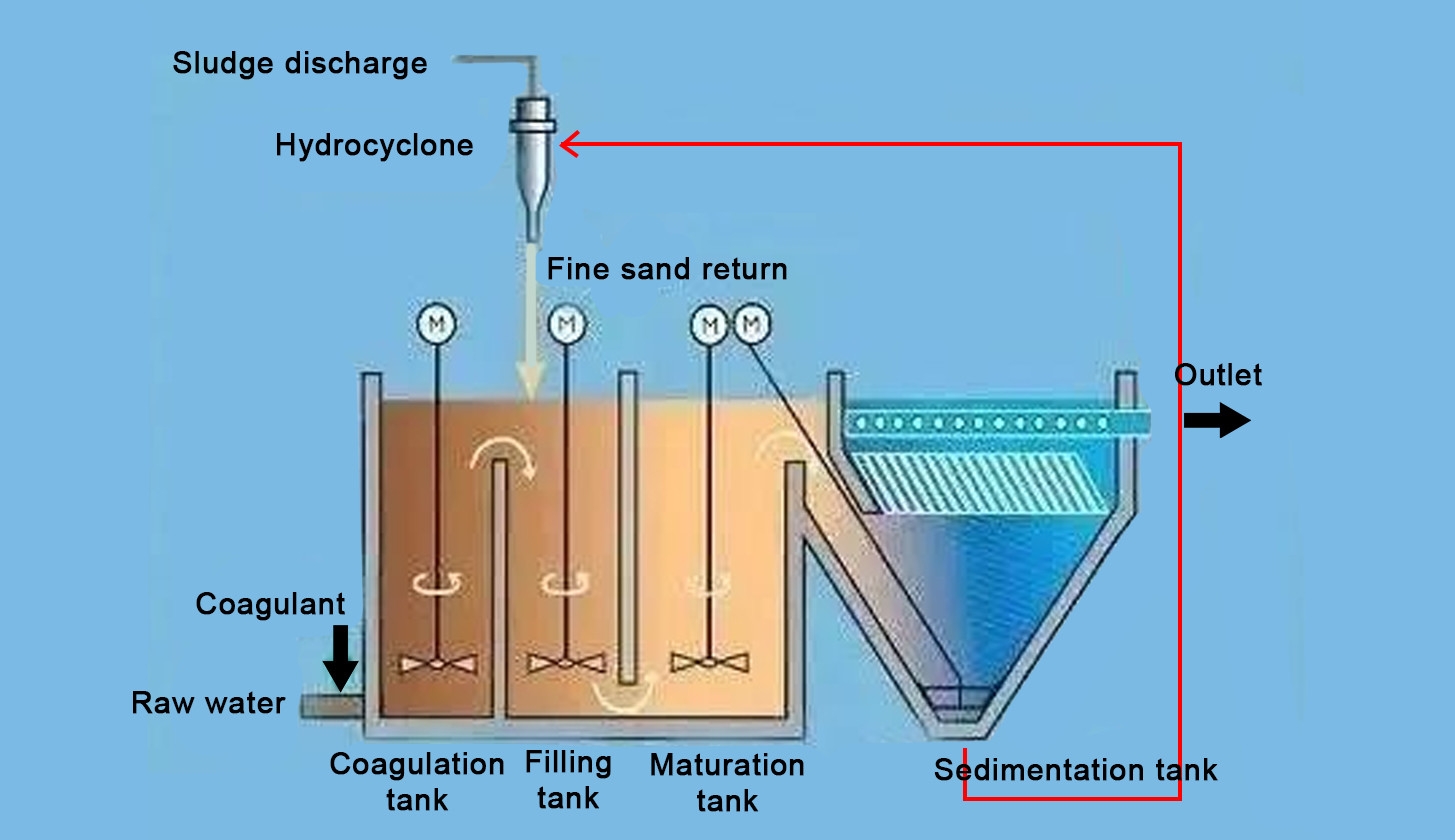
Working Principle of Inclined Plate Settler
The inclined plate settler, also called a shallow-depth sedimentation tank, consists of parallel plates installed at a 45°–60° inclination.
Wastewater flows upward through the channels between the plates, while suspended solids settle on the plates and slide down into the sludge hopper.
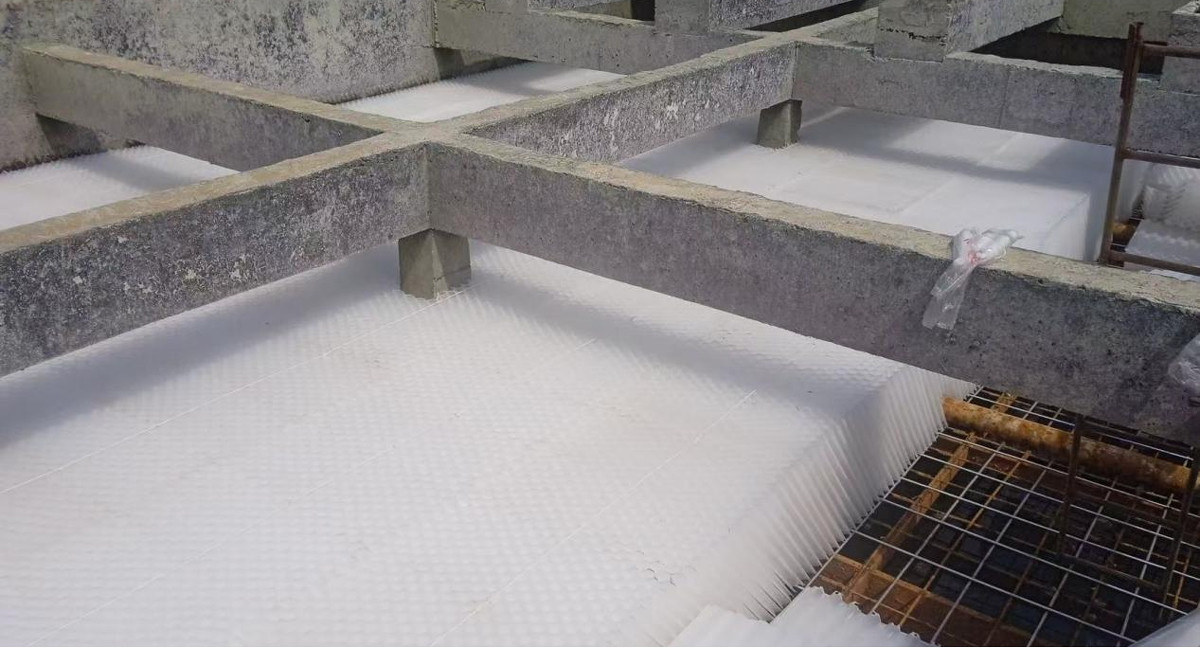

II. Internal Structure
The system consists of:
*Inclined Plate/Tube Sedimentation Zone (60° inclination, length ~1.0 m, plate spacing/tube diameter 80–100 mm)
*Inlet Distribution Zone
*Clear Water Outlet Zone (water depth 0.7–1.0 m)
*Buffer Zone
*Sludge Zone (bottom buffer layer height 1.0 m)

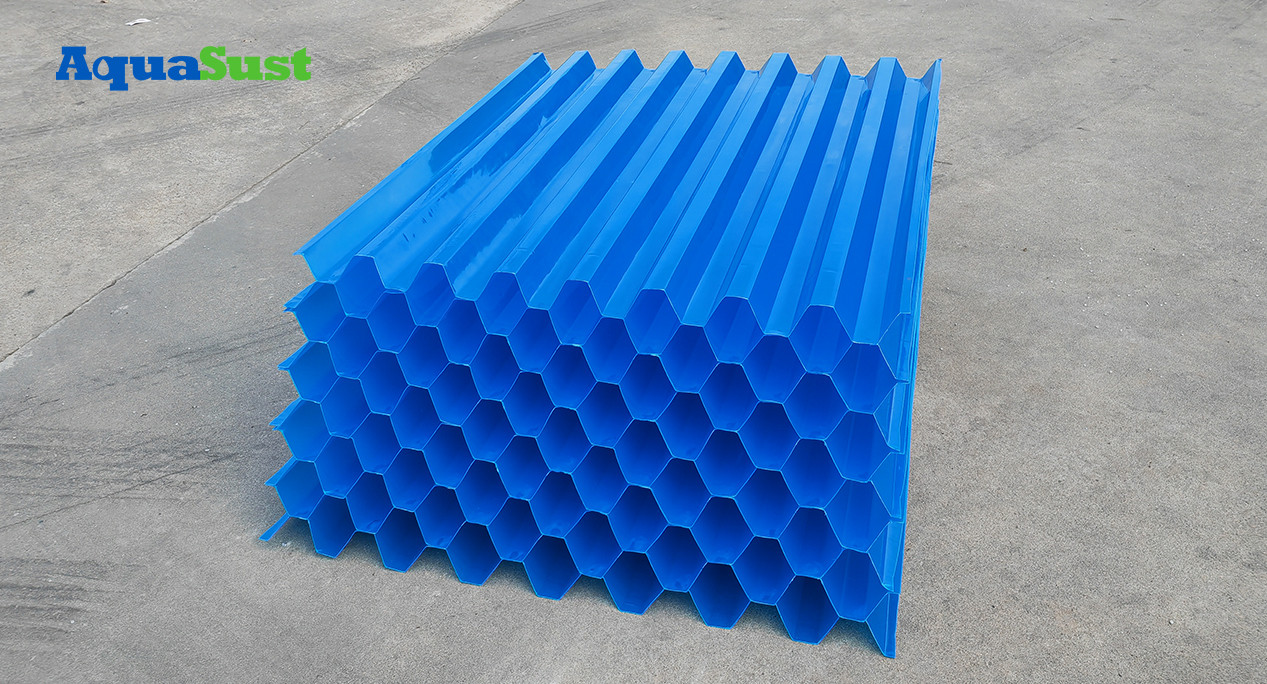
Materials for Inclined Tubes/Plates:
Lightweight, thin-walled, durable, non-toxic, and cost-effective materials such as plastic, fiberglass, or asbestos-cement coated with resin. The tubes can be arranged in a honeycomb pattern, forming an inclined tube sedimentation tank.
The inclined plate/tube settler divides the sedimentation zone into multiple shallow layers using parallel inclined tubes or plates (sometimes with honeycomb fillers).
Depending on the flow direction relative to sludge settling, it can be categorized as:
(1)Counter-current flow
(2)Co-current flow
(3)Cross-flow
Each pair of parallel plates (or tubes) functions as a miniature sedimentation tank.

III. Advantages of Inclined Plate/Tube Settlers
(1)Utilizes laminar flow principles, enhancing treatment capacity.
(2)Reduces particle settling distance, shortening sedimentation time.
(3)Increases effective sedimentation area, improving efficiency.
IV. Applications
Inclined plate/tube settlers can serve as auxiliary equipment for processes like flotation or evaporation, or as standalone treatment units for various wastewater types, including:
(1)Electroplating Wastewater – Removes >90% of heavy metals (Cr, Cu, Fe, Zn, Ni), meeting discharge standards.
(2)Coal Mining/Mineral Processing Wastewater – Reduces turbidity from 500–1500 mg/L to 5 mg/L.
(3)Textile/Dyeing Wastewater – 70–90% color removal, 50–70% COD reduction.
(4)Tannery/Food Industry Wastewater – Removes 50–80% COD and >90% suspended solids.
(5)Chemical Wastewater – 60–70% COD removal, 60–90% decolorization, and compliant SS levels.
V. Key Benefits
1.Simple structure, no vulnerable parts, long service life, minimal maintenance.
2.Stable operation, easy to control.
3.Low energy consumption, cost-effective.
4.Compact footprint, low investment, rapid deployment, high efficiency.

